Publications
Discover the research findings of IndustoAI in various applications of AI/ML and automation.
deep anomaly detection and segmentation
Deep Local Feature Matching Image Anomaly Detection with Patch Adaptive Average Pooling Technique
Author(s): Afshin Dini, Esa Rahtu
Year: 2025
Link: Paper
Abstract: We present a new visual defect detection approach based on a deep feature-matching model and a patch adaptive technique. The main idea is to utilize a pre-trained feature-matching model to identify the training sample(s) being most similar to each test sample. By applying a patch-adaptive average pooling on the extracted features and defining an anomaly map using a pixel-wise Mahalanobis distance between the normal and test features, anomalies can be detected properly. By evaluating our method on the MVTec dataset, we discover that our method has many advantages over similar techniques as (1) it skips the training phase and the difficulties of fine-tuning model parameters that may vary from one dataset to another, (2) it performs quite well on datasets with only a few training samples, reducing the costs of collecting large training datasets in real-world applications, (3) it can automatically adjust itself without compromising performance in terms of shift in data domain, and (4) the model’s performance is better than similar state-of-the-art methods.
Keyword(s): Anomaly Detection, Deep Local Feature Matching, MVTec-AD Dataset.

Detecting Anomalies in Textured Images Using Modified Transformer Masked Autoencoder
Author(s): Afshin Dini, Esa Rahtu
Year: 2024
Link: Paper
Abstract: We present a new method for detecting and locating anomalies in textured-type images using transformer-based autoencoders. In this approach, a rectangular patch of an image is masked by setting its value to gray and then fetched into a pre-trained autoencoder with several blocks of transformer encoders and decoders in order to reconstruct the unknown part. It is shown that the pre-trained model is not able to reconstruct the defective parts properly when they are inside the masked patch. In this regard, the combination of the Structural Similarity Index Measure and absolute error between the reconstructed image and the original one can be used to define a new anomaly map to find and locate anomalies. In the experiment with the textured images of the MVTec dataset, we discover that not only can this approach find anomalous samples properly, but also the anomaly map itself can specify the exact locations of defects correctly at the same time. Moreover, not only is our method computatio nally efficient, as it utilizes a pre-trained model and does not require any training, but also it has a better performance compared to previous autoencoders and other reconstruction-based methods. Due to these reasons, one can use this method as a base approach to find and locate irregularities in real-world applications.
Keyword(s): Anomaly Detection, Anomaly Localization, Masked Autoencoders.

Anomaly Detection and Localization for Images of Running Paper Web in Paper Manufacturing
Author(s):Afshin Dini, Marja Mettänen, Esa Rahtu
Year: 2024
Link: Paper
Abstract: We introduce a new method based on convolutional autoencoders to detect and locate paper web anomalies that can cause web breaks during the paper production process. In this approach, we pre-process the images, captured by two high-speed cameras located at the opposite sides of the running paper web at a paper machine, in several steps to remove noises and separate the paper web areas from the background. After designing and training a convolutional autoencoder with non-anomalous samples, a novel anomaly score and map are defined to find and locate web irregularities based on an edge detector and a reconstruction error, defined by the combination of absolute error and Structural Similarity Index Measure between the reconstructed and the original images, in each test sample. By assessing the proposed approach on the images taken from a real paper machine, we discover that this method can detect paper defects properly and, therefore it has the potential to improve machine functionality and even to prevent certain types of web breaks, which reduces the machine downtime, paper losses, maintenance costs, and energy consumption, i.e., increases the performance and efficiency of paper machinery.
Keyword(s): Anomaly Detection, Anomaly Localization, Running Paper Web Defects, Paper Manufacturing.

Visual Anomaly Detection and Localization with a Patch-Wise Transformer and Convolutional Model
Author(s):Afshin Dini, Esa Rahtu
Year: 2023
Link: Paper
Abstract: We present a one-class classification approach for detecting and locating anomalies in vision applications based on the combination of convolutional networks and transformers. This method utilizes a pre-trained model with four blocks of patch-wise transformer encoders and convolutional layers to extract patch embeddings from normal samples. The patch features from the third and fourth blocks of the model are then combined together to form the final representations, and then several multivariate Gaussian distributions are mapped on these normal embeddings accordingly. At the testing phase, irregularities are detected and located by setting a threshold on anomaly score and map defined by calculating the Mahalanobis distances between the patch embeddings of test samples and the related normal distributions. By evaluating the proposed method on the MVTec dataset, we find out that not only can this method detect anomalies properly due to the ability of the convolutional and transformer layers to present local and overall properties of an image, respectively, but also it is computationally efficient as it skips the training phase by using a pre-trained network as the feature extractor. These properties make our method a good candidate for detecting and locating irregularities in real-world industrial applications.
Keyword(s): Anomaly Detection, Anomaly Localization, Combined Transformer and Convolutional Networks.

TPSAD: Learning to Detect and Localize Anomalies With Thin Plate Spline Transformation
Author(s):Afshin Dini, Esa Rahtu
Year: 2022
Link: Paper
Abstract: We present a self-supervised learning approach with a novel proxy task, based on thin-plate spline transformation, for detecting and localizing anomalies in images. The self-supervised model, referred as TPSAD, is firstly optimized to classify normal examples from the artificially anomalous ones which are created by a new data augmentation technique that applies random thinplate spline transformation to a patch of an image, selected by the Canny edge detector. Then, the last layer representations of the model are utilized for detecting anomalies with the Gaussian density estimator technique, while the middle layer representations are used for localizing anomalies. By assessing the proposed method on the MVTec dataset, we discover that not only can it detect anomalous images and localize irregularities properly, but also it is computationally efficient in both training and testing stages, compared to previous methods. Moreover, the method is robust to images containing unaligned objects due to the usage of the Canny edge algorithm in proxy task learning. Lastly, high performance in addition to low computational cost makes our method a good candidate for image anomaly detection in industrial applications.
Keyword(s): Anomaly detection, Anomaly localization, Selfsupervised learning, Thin plate spline transformation, Canny edge detector.

Unsupervised Detection of Anomalous Sound for Machine Monitoring Under Domain Shifted Condition Based on GANs and Autoencoders
Author(s): Amirhossein Hassankhani, Afshin Dini, Konstantinos Drossos
Year: 2021
Link: Paper
Abstract: This report presents an unsupervised method for detecting anomalous industrial machine sounds, taken under two different conditions and shifted domains, and submitted to DCASE 2021 Task 2. The method tries to map the distribution of data into a learned latent space, using a reconstructive autoencoder followed by an additional second encoder. Furthermore, the method employs a discriminator trying to differentiate between the input and the reconstructed audio to and from the autoencoder. All components are jointly optimized, using a sum of weighted losses and utilizing an adversarial setting between the autoencoder and the discriminator. Anomaly is detected through the distance between the output of the two encoders. Obtained results show that the method performs better than the provided baseline in some cases.
Keyword(s): Anomaly detection, generative adversarial network, domain adaptation, GAN, autoencoder.

large language models (LLM) in industries
ChatGPT or A Silent Everywhere Helper: A Survey of Large Language Models
Author(s): Azim Akhtarshenas, Afshin Dini, Navid Ayoobi
Year: 2025
Link: Paper
Abstract: Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing Natural Language Processing (NLP), with Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer (ChatGPT) standing out as a notable example due to its advanced capabilities and widespread applications. This survey provides a comprehensive analysis of ChatGPT, exploring its architecture, training processes, and functionalities. We examine its integration into various domains across industries such as customer service, education, healthcare, and entertainment. A comparative analysis with other LLMs highlights ChatGPT’s unique features and performance metrics. Regarding benchmarks, the paper examines ChatGPT’s comparative performance against other LLMs and discusses potential risks such as misinformation, bias, and data privacy concerns. Additionally, we offer a number of figures and tables that outline the backdrop of the discussion, the main ideas of the article, the numerous LLM models, a thorough list of datasets used for pre-training, fine-tuning, and evaluation, as well as particular LLM applications with pertinent references. Finally, we identify future research directions and technological advancements, underscoring the evolving landscape of LLMs and their profound impact on artificial intelligence Artificial Intelligence (AI) and society.

Control System Design and Estimation
Automatic Estimation of Excavator’s Actual Productivity in Trenching and Grading Operations Using Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Author(s): Amirmasoud Molaei, Antti Kolu, Niko Haaraniemi, Prof. Marcus Geimer
Year: 2023
Link: Paper
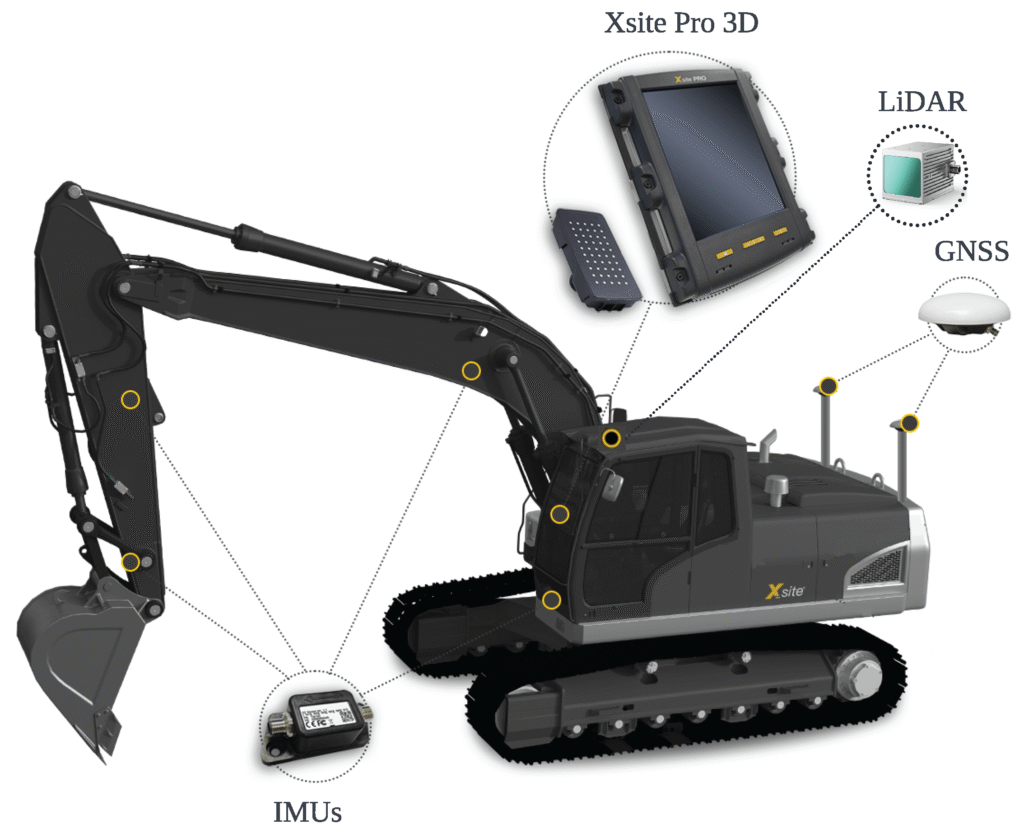
Abstract: This paper discusses the excavator’s actual productivity in trenching and grading operations. In these tasks, the quantity of material moved is not significant; precision within specified tolerances is the key focus. The manual methods for productivity estimation and progress monitoring of these operations are highly time-consuming, costly, error-prone, and labor-intensive. An automatic method is required to estimate the excavator’s productivity in the operations. Automatic productivity tracking aids in lowering time, fuel, and operational expenses. It also enhances planning, detects project problems, and boosts management and financial performance. The productivity definitions for trenching and grading operations are the trench’s length per unit of time and graded area per unit of time, respectively. In the proposed techniques, a grid-based height map (2.5D map) from working areas is obtained using a Livox Horizon® light detection and ranging (LiDAR) sensor and localization data from the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and inertial measurement units (IMUs). Additionally, building information modeling (BIM) is utilized to acquire information regarding the target model and required accuracy. The productivity is estimated using the map comparison between the working areas and the desired model. The proposed method is implemented on a medium-rated excavator operated by an experienced operator in a private worksite. The results show that the method can effectively estimate productivity and monitor the development of operations. The obtained information can guide managers to track the productivity of each individual machine and modify planning and time scheduling.
Keyword(s): Excavator’s productivity, progress monitoring, grading operation, trenching operation, elevation terrain mapping, Building Information Modeling (BIM)
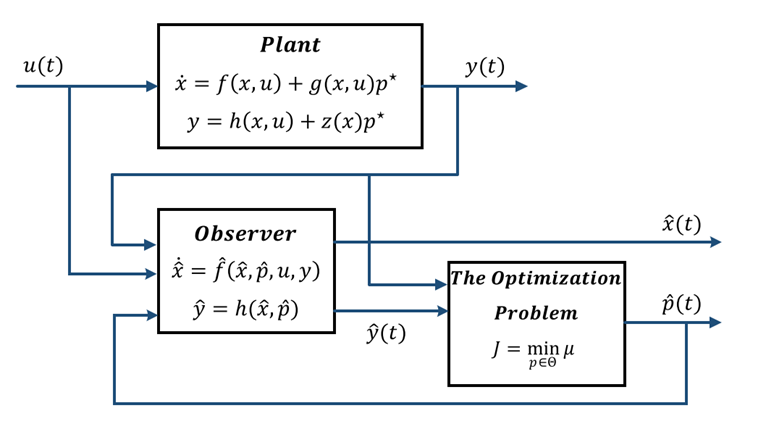
Parameter and State Estimation of Managed Pressure Drilling System Using the Optimization-Based Supervisory Framework
Author(s): Amirmasoud Molaei, Amirhossein Nikoofard, Ali Khaki Sedigh, and Lars Imsland
Year: 2023
Link: Paper
Abstract: This brief proposes a method for the simultaneous estimation of unknown parameters and unmeasured states of nonlinear continuous-time systems. The proposed methodology has been inspired by the supervisory estimation approaches that use a bank of observers and are designed based on a set of fixed nominal parameter values. Consequently, the methods have a high computational load, and the estimated parameters marginally converge to the true parameters. For the reduction of computational load, a new objective function with a lower computational load that is computed during a sliding time window is proposed. Then, an observer with an optimization-based framework is introduced for nonlinear systems with affine unknown parameters, that replaces the bank of observers with a single observer. The unknown parameters update is based on the defined objective function. The performance of the method is illustrated in a simulation study of a managed pressure drilling (MPD) system. In the MPD process, downhole measurements encounter problems such as transmission delay and slow sampling rate. Also, the drilling process has parametric uncertainties due to the unknown friction coefficient. The simulation results indicate that the simultaneous estimations of the friction coefficient and drill bit flow rate in the MPD system converge to their true values in finite time.
Keyword(s): Affine Unknown Parameters, Managed Pressure Drilling (MPD), Optimization, Parametric Uncertainty.
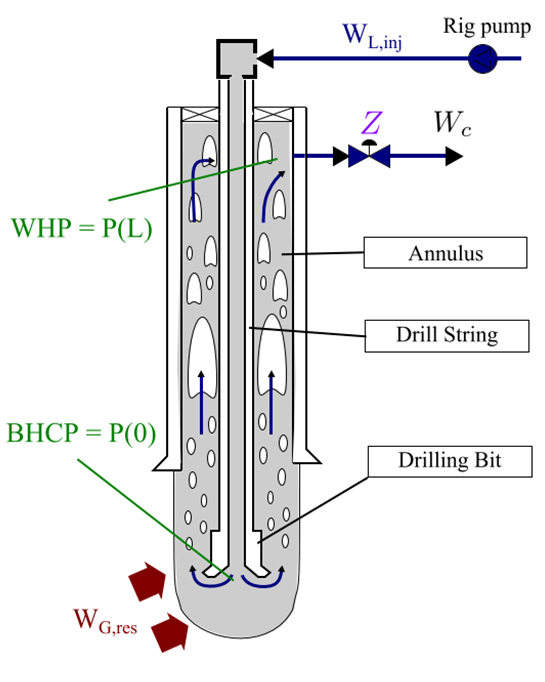
Reservoir Characterization in Under-balanced Drilling with Noninear Moving Horizon Estimation with Manual and Automatic Control Conditions
Author(s): Amirhossein Nikoofard, Tor Arne Johansen, and Amirmasoud Molaei
Year: 2020
Link: Paper
Abstract: This paper discusses the state estimation of the Under-Balanced Drilling (UBD) system in the presence of parametric uncertainties. During this process, the production indices of oil and gas from the reservoir into the well in the manual and automatic control conditions are estimated by employing the nonlinear Moving Horizon Estimation (MHE) based on a low-order lumped (LOL) model. The LOL model has a low computational load and is suitable for reservoir characterization during UBD operations. The estimation algorithms are tested by using a difficult scenario which is created by the OLGA multiphase flow simulator. The simulation results indicate that the nonlinear MHE has a high performance and can identify the production indices of gas and oil. Moreover, the method has the capability to diagnose the rapid variation of the production constant in different conditions, such as working with a manual or automatic controller. The results of the scenario with the swift change in the production index of gas demonstrate that the nonlinear MHE has a higher performance than the Unscented Kalman Filter (UKF). The effect of uncertainties and errors in the reservoir and well parameters on the nonlinear MHE is evaluated. It is revealed that the presence of parametric uncertainty in the reservoir pore pressure can significantly affect the estimators’ performance.
Keyword(s): Under-balanced Drilling, OLGA Multi-Phase Flow Simulator, Low-order Lumped model, Moving Horizon Estimation, Nonlinear Estimation
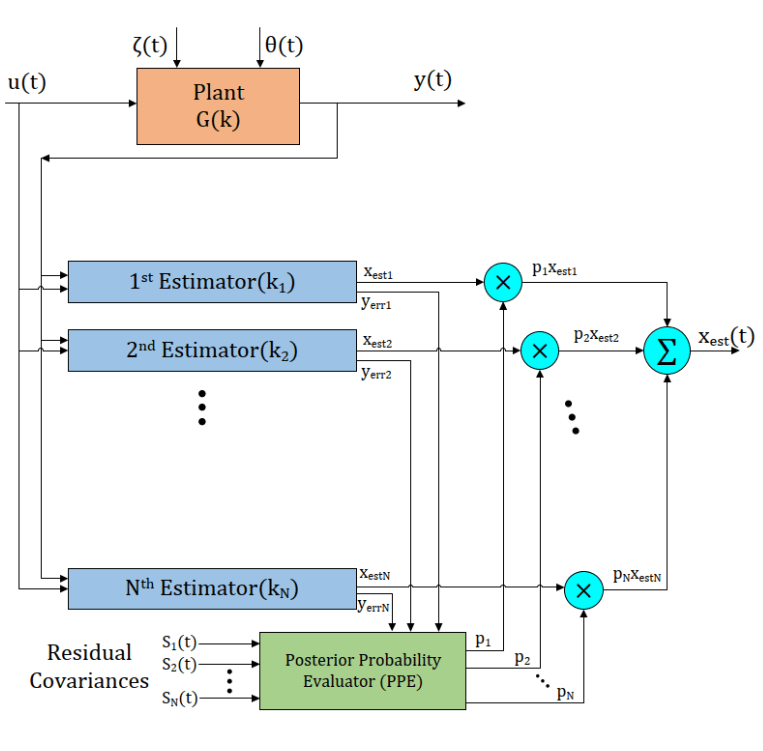
Managed Pressure Drilling System State Estimation Using The Multiple Model Adaptive Estimation Approach
Author(s): Amir Masoud Molaei, Amir Hossein Nikoofard, Ali Khaki-Sedigh, and Lars Imsland
Year: 2020
Link: Paper
Abstract: This paper studies state estimation in the presence of parametric uncertainties, with flow estimation in Managed Pressure Drilling as a case study. Downhole measurements in most MPD systems have low frequency due to communication with mud-pulse telemetry. Also, the drilling process has parametric uncertainties due to unknown friction and fluid density and unmodeled actuator dynamics and noise add to the system complexity. This paper proposes a bank of estimators for simultaneous estimation of the model states. A Multiple-Model Adaptive Estimation (MMAE) algorithm is presented that encompasses a bank of Kalman Filters (KFs). Each KF is designed to handle a specific segment of the parametric uncertainty. In this algorithm, a probabilistically weighted combination of the local state estimations is used. Simulation results reveal that the proposed method can satisfactory estimate the unmeasured states in the presence of a wide range of uncertainties. Finally, the MMAE method is compared with a supervisory estimation algorithm to further clarify technical issues in the MPD system state estimation problem.
Keyword(s): Managed pressure drilling (MPD), multiple model adaptive estimation (MMAE), supervisory estimation, parameter uncertainty.
A novel framework for the estimation of excavator’s actual productivity in the grading operation using Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Author(s): Amirmasoud Molaei, Prof. Marcus Geimer, and Antti Kolu
Year: 2023
Link: Paper
Abstract: TThis paper discusses the productivity of an excavator in the grading operation. Although the grading operation is one of the most important tasks in various worksites, there is no automated algorithm to calculate the excavator’s productivity during the grading operation. Manual methods for measuring the height of ground are highly time-consuming, labor-intensive, and error-prone. In the presented method, a height map from surrounding areas is provided using a light detection and ranging (LiDAR) sensor every few seconds. The proposed approach utilizes building information modeling (BIM) to retrieve information about the desired shape of the surface and the required accuracy. The results of the presented method are shown by implementation on a collected dataset using an excavator.
Keyword(s): Excavator’s productivity, grading operation, elevation terrain mapping, building information modeling (BIM)
Machine Learning in Heavy Duty Mobile Machines (HDMMs)
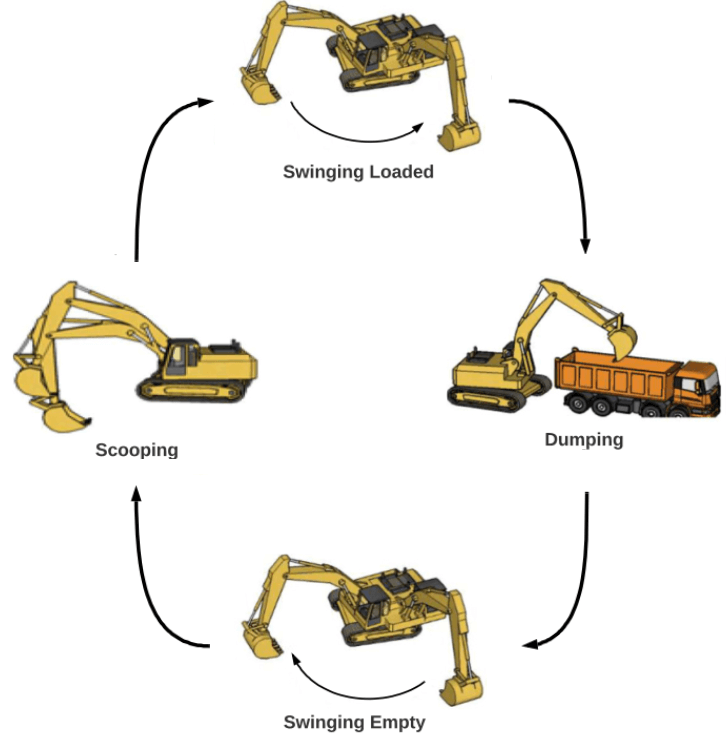
Automatic recognition of excavator working cycles using supervised learning and motion data obtained from inertial measurement units (IMUs)
Author(s): Amirmasoud Molaei, Antti Kolu, Kalle Lahtinen, and Prof. Marcus Geimer
Year: 2024
Link: Paper
Abstract: This paper proposes an automatic method for excavator working cycle recognition using supervised classification methods and motion information obtained from four inertial measurement units (IMUs) attached to moving parts of an excavator. Monitoring and analyzing tasks that have been performed by heavy-duty mobile machines (HDMMs) are significantly required to assist management teams in productivity and progress monitoring, efficient resource allocation, and scheduling. Nevertheless, traditional methods depend on human observations, which are costly, time-consuming, and error-prone. There is a lack of a method to automatically detect excavator major activities. In this paper, a data-driven method is presented to identify excavator activities, including loading, trenching, grading, and idling, using motion information, such as angular velocities and joint angles, obtained from moving parts, including swing body, boom, arm, and bucket. Firstly, a dataset lasting 3 h is collected using a medium-rated excavator. One experienced and one inexperienced operator performed tasks under different working conditions, such as different types of material, swing angle, digging depth, and weather conditions. Four classification methods, including support vector machine (SVM), k-nearest neighbor (KNN), decision tree (DT), and naive Bayes, are off-line trained. The results show that the proposed method can effectively identify excavator working cycles with a high accuracy of 99%. Finally, the impacts of parameters, such as time window, overlapping configuration, and feature selection methods, on the classification accuracy are comprehensively analyzed.
Keyword(s): Activity recognition, Excavator, Earth-moving operations, Supervised learning, Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)
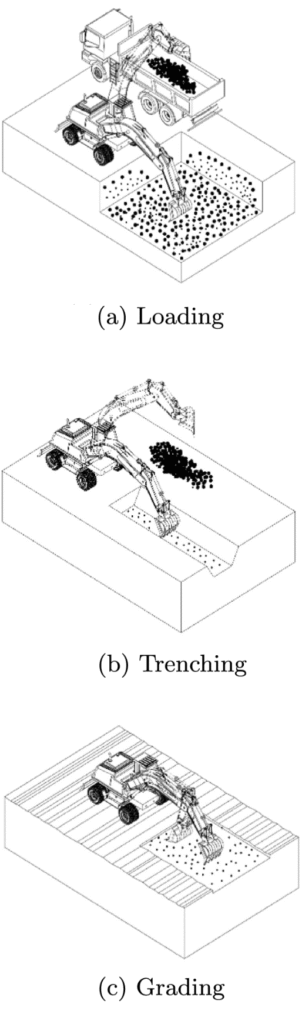
Automatic estimation of excavator actual and relative cycle times in loading operations
Author(s): Amirmasoud Molaei, Antti Kolu, Kalle Lahtinen, and Prof. Marcus Geimer
Year: 2023
Link: Paper
Abstract: This paper proposes a framework to automatically determine the productivity and operational effectiveness of an excavator. The method estimates the excavator’s actual, theoretical, and relative cycle times in the loading operation. Firstly, a supervised learning algorithm is proposed to recognize excavator activities using motion data obtained from four inertial measurement units (IMUs) installed on different moving parts of the machine. The classification algorithm is offline trained using a dataset collected via an excavator operated by two operators with different levels of competence in different operating conditions. Then, an approach is presented to estimate the cycle time based on the sequence of activities detected using the trained classification model. Since operating conditions can significantly influence the cycle time, the actual cycle time cannot solely reveal the machine’s performance. Hence, a benchmark or reference is required to analyze the actual cycle time. In the second step, the theoretical cycle time of an excavator is automatically estimated based on the operating conditions, such as swing angle and digging depth. Furthermore, two schemes are presented to estimate the swing angle and digging depth based on the recognized excavator activities. In the third step, the relative cycle time is obtained by dividing the theoretical cycle time by the actual cycle time. Finally, the results of the method are demonstrated by the implementation on two case studies which are operated by inexperienced and experienced operators. The obtained relative cycle time can effectively monitor the performance of an excavator in loading operations. The proposed method can be highly beneficial for worksite managers to monitor the performance of each machine in worksites.
Keyword(s): Excavator, Productivity estimation, Activity recognition, Cycle time estimation, Swing angle, Digging depth, Loading operation