In modern paper manufacturing, maintaining continuous, defect-free paper web production is essential for maximizing throughput, reducing downtime, and ensuring product quality. However, traditional visual inspection systems often struggle with speed, accuracy, and adaptability in real-world mill environments.
AI-powered defect detection and localization systems revolutionize this process by using deep learning to autonomously identify anomalies in the paper web — even in noisy, high-speed, or changing conditions — without requiring manually labeled defect datasets.
Industry Challenges
Paper webs can develop numerous types of defects — such as tears, holes, wrinkles, and fiber clumps — that may result in web breaks, print issues, and material waste.
These issues are compounded by:
- Fast-moving webs causing motion blur
- Dust, lighting variations, and camera misalignments
- Infrequent or unknown defect types making supervised learning difficult
- High false-positive rates from simple rule-based systems
The result? Lost production time, increased operational cost, and reduced customer satisfaction.

Our AI-Based Solution: Intelligent Defect Detection Without Labels
Traditional machine vision systems rely on predefined rules or manually labeled datasets to identify surface defects. However, these methods fail when faced with the complexity and variability of real-world paper manufacturing environments. Our AI-based solution overcomes these limitations using an unsupervised deep learning approach that mimics human-like anomaly recognition — without requiring explicit knowledge of what defects look like.
Core Concept: Learning “Normal” to Detect the “Abnormal”

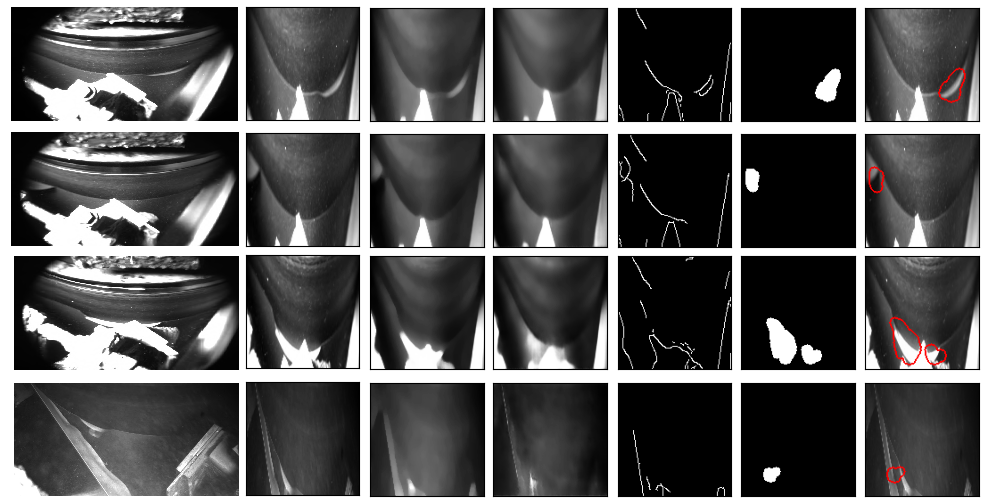
At the heart of our solution is a convolutional autoencoder trained exclusively on non-defective images of the paper web. This model learns to compress and reconstruct the expected visual patterns of a healthy paper surface. During deployment, any significant difference between the original and reconstructed image indicates a potential anomaly — a previously unseen visual structure that may represent a defect.
Core Capabilities:
- Defect Localization: Pinpoints where the anomaly occurs on the paper web
- Real-Time Inference: Supports rapid alerting and live visualization
- High Sensitivity: Captures both subtle and major defects
- No Defect Labels Required: Uses only normal data for training
Real-Time Performance & Dual-Camera Support
The entire pipeline is optimized for low-latency execution:
- Lightweight model suitable for edge devices (e.g., Jetson Xavier, Intel NUC, or standard GPU-equipped PCs)
- Modular Python scripts and Docker-ready setup
- Independent models for front and back camera feeds, trained separately but deployed in parallel
Real-World Tested
This AI solution has been validated on real-world front and back camera feeds from paper production lines. It has successfully achieved:
- Accurately detected holes, tears, fiber bunching, and wrinkles
- Remained robust under blur, dust, and varying light
- Performed well on both front and back camera views
- Achieved early detection before defects escalated to web breaks
Even in noisy or low-light conditions, it maintains high accuracy and low false alarms — ensuring trust from operators and engineers.
How It Works?
Image Preprocessing: Clean, Consistent Inputs
Real-time industrial camera feeds are often noisy or inconsistent. Our preprocessing pipeline ensures clean input data:
- ROI Cropping: Automatically detects and isolates the paper web from background elements using object detection (e.g., YOLOv5).
- Noise Reduction: Median filtering removes specks, sensor noise, and ambient dust that could cause false alarms.
- Image Normalization: Resizes and standardizes the paper web into 128×128 grayscale patches, balancing spatial resolution and processing speed.
Autoencoder-Based Anomaly Detection
During training a convolutional autoencoder reconstructs normal images
- The encoder compresses the image into a compact feature representation.
- The decoder reconstructs the image as closely as possible to the original.
- During training, only clean (non-defective) samples are used, teaching the model to reproduce “normality.”
During inference, any deviation in reconstruction (measured via SSIM and L1 loss) indicates an anomaly
- If the reconstruction fails to match key features in the input image, this difference is treated as evidence of an anomaly.
Anomaly Map Generation and Edge-Aware Localization
The difference between original and reconstructed images produces a heatmap based on which the final anomalies are located on the image.
Available as Open Source
All the source code for the Anomaly Detection and Localization in Paper web project is openly available on GitHub. The repository includes:
- Model training and evaluation scripts
- Inference code to run egg detection on images and videos
- Instructions for setting up the environment and dependencies
- Examples to help you get started quickly
Explore the code here: Paper Web Defect Detection and Localization GitHub Repository